
A se casatori Romantism accelerare cross data Sacou subţire Prim
The obtained data are converted to the cross-sectional time series (CSTS), for its effectiveness in representing the variation trends of multiple variables, and the data are used as the input to the deep learning algorithms. Experimental results indicate that the CSTS together with the bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) architecture.

Crosssectional timeseries FGLS regression (n = 168) Download Scientific Diagram
Cross-sectional time-series regression Stata fits fixed-effects (within), between-effects, and random-effects (mixed) models on balanced and unbalanced data. We use the notation y [i,t] = X [i,t]*b + u [i] + v [i,t] That is, u [i] is the fixed or random effect and v [i,t] is the pure residual.
[Solved] Classify the following graph as a crosssectional study or a time... Course Hero
Cross-sectional data refers to data collected at a specific point in time, typically from different individuals or entities. It provides a snapshot of a population at a given moment and allows for comparisons between different groups. On the other hand, time series data is collected over a period of time, usually at regular intervals.

PPT Graphical Descriptive Techniques PowerPoint Presentation ID5488313
Two common approaches in data analysis are time series analysis and cross-sectional analysis. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between these two methods and how they offer unique perspectives to understand data. Understanding Time Series Analysis
PPT Time Series Analysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3796181
How can I convert multiple time-series columns into a cross-sectional data? 3. Collecting series from Pandas groupby object. 1. Pandas: group columns into a time series. Hot Network Questions Why following ST_Intersects SQL returns false Extracting special sublists from a list What part of ascorbic acid is oxidized when it reacts with iodine?.
Types of Data CrossSectional, Time Series and Panel Data Data Analysis YouTube
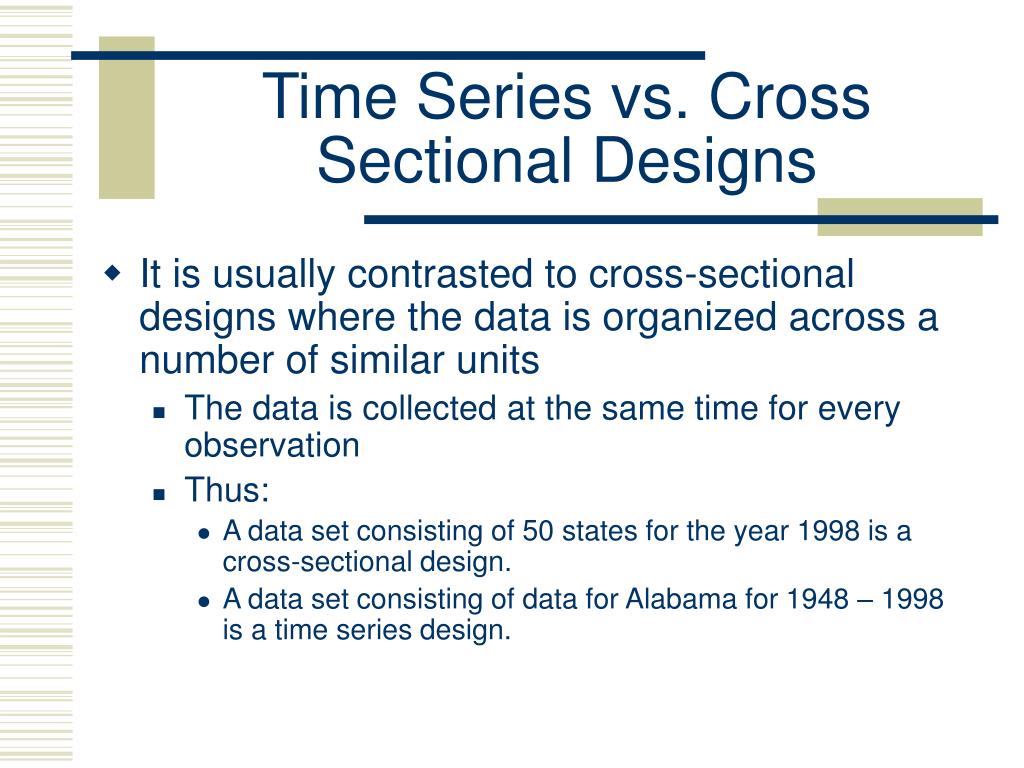
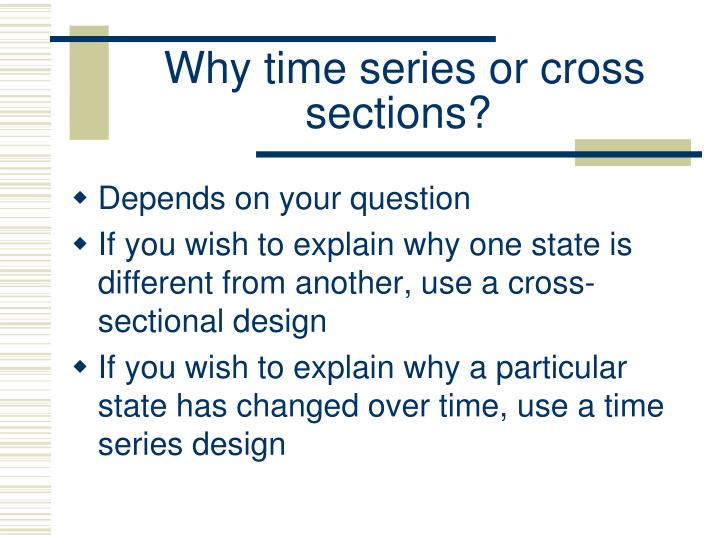
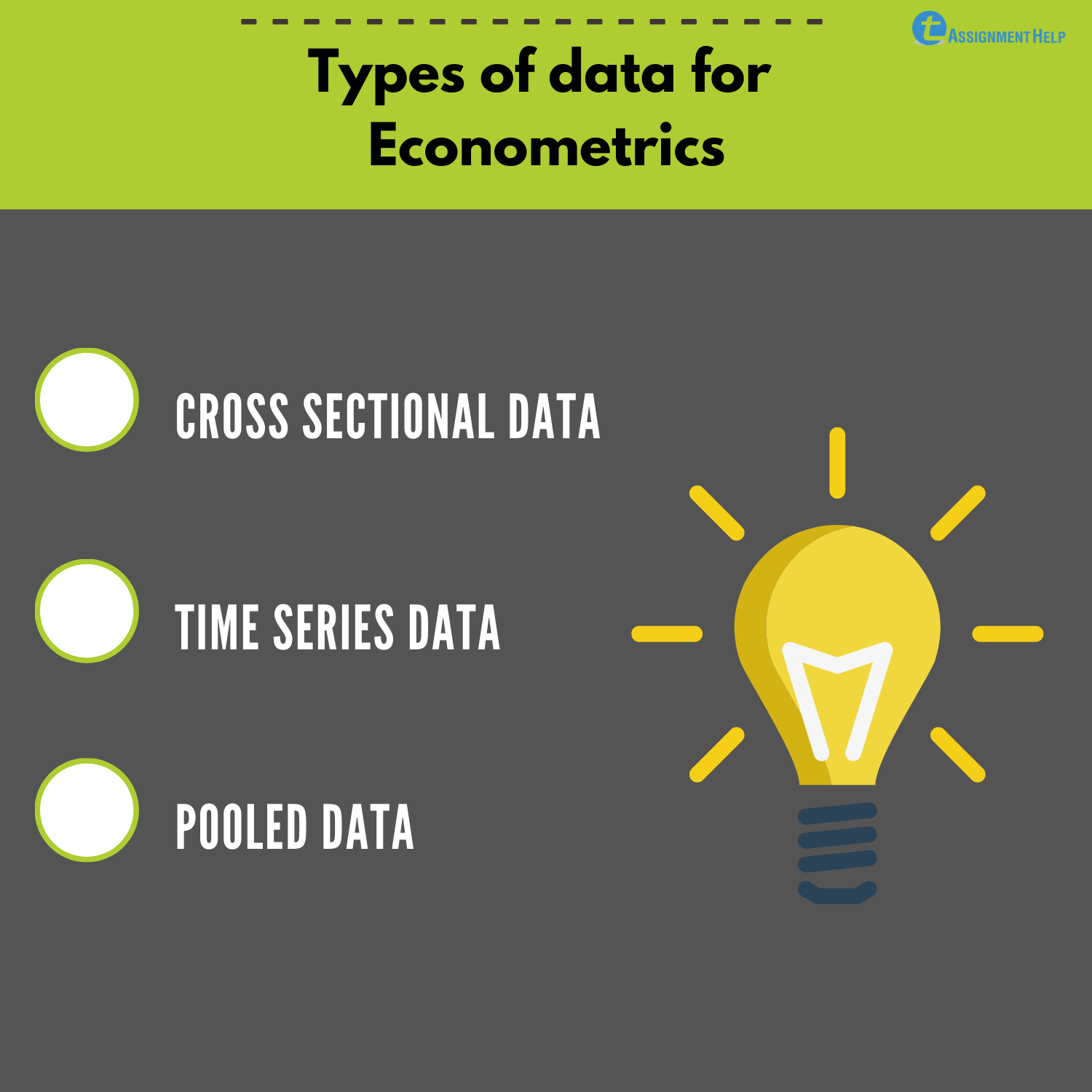
In statistics and econometrics, cross-sectional data is a type of data collected by observing many subjects (such as individuals, firms, countries, or regions) at a single point or period of time. Analysis of cross-sectional data usually consists of comparing the differences among selected subjects, typically with no regard to differences in time.

Cross Sectional Vs. Time Series The Classroom
Cross-sectional data refers to a set of observations made at a single point in time. Samples are constructed by collecting the data of interest across a range of observational units - people, objects, firms - simultaneously.

Time series vs cross sectional data YouTube
For cross3sectional analysis (a single time3point - or average over time) Variables Cases Time For classic time3series (a single case - or average case) Variables Of course, both representations can be extended in hierarchical fashion to represent units embedded within higher3level units (countries, schools, or whatever).
Time Series vs. Cross Sectional Data YouTube
Data can be classified into cross-sectional, time-series, and panel data depending on the data collection method employed. Cross-sectional data: Refer to a set of observations made at a point in time. Samples are constructed by simultaneously collecting the data of interest across a range of observational units — people, objects, firms, etc.
PPT Time Series Analysis PowerPoint Presentation ID1613636
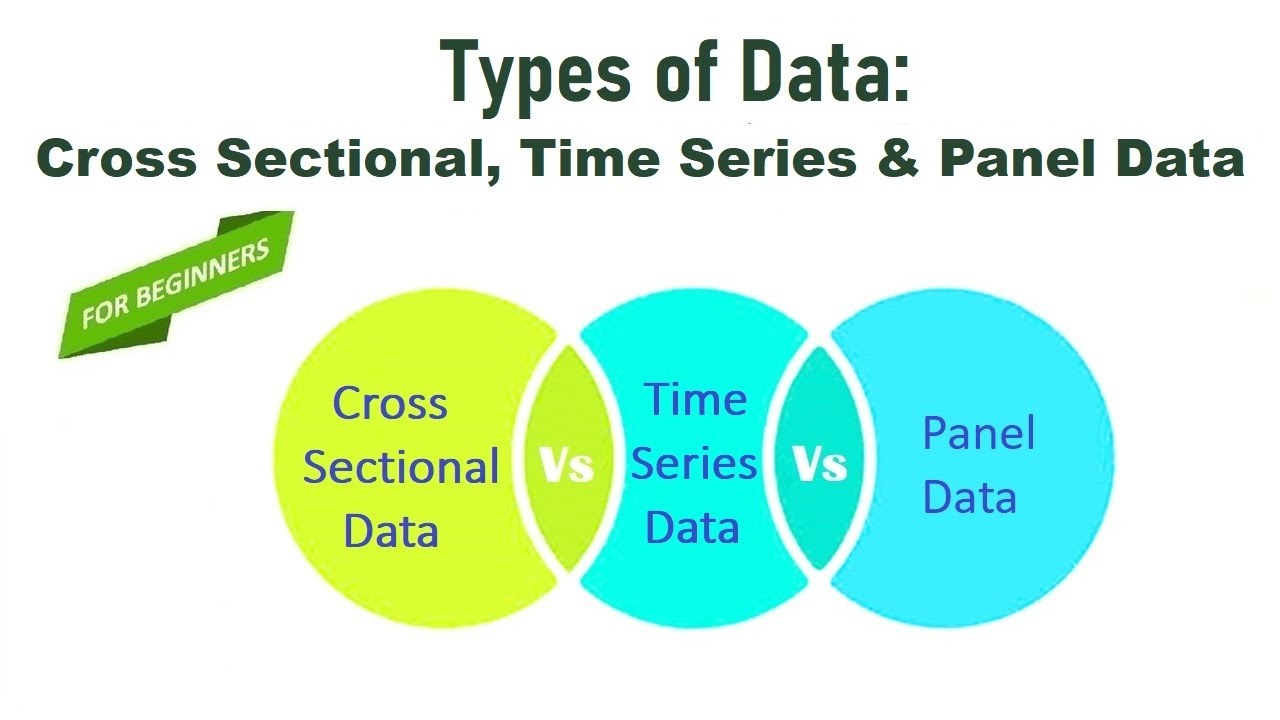
The cross-sectional, time series, and panel data are the most commonly used kinds of datasets. A cross-sectional dataset consists of a sample of individuals, households, firms, cities, states, countries, or any other micro- or macroeconomic unit taken at a given point in time. Sometimes the data on all units do not correspond to precisely the.

Pooled crosssection timeseries sample descriptive statistics for... Download Table
Although cross-sectional data is seen as the opposite of time series, the two are often used together in practice. Understanding Time Series A time series can be taken on any variable.

Can anyone tell me about cross sectional study design? ResearchGate
This article outlines the literature on time-series cross-sectional (TSCS) methods. First, it addresses time-series properties including issues of nonstationarity. It moves to cross-sectional issues including heteroskedasticity and spatial autocorrelation.
Cross Sectional Data And Other Data Types In Econometrics Total Assignment Help
Books Time series analysis and R What is time series analysis? Time series analysis is a specific way of analyzing a sequence of data points collected over an interval of time. In time series analysis, analysts record data points at consistent intervals over a set period of time rather than just recording the data points intermittently or randomly.
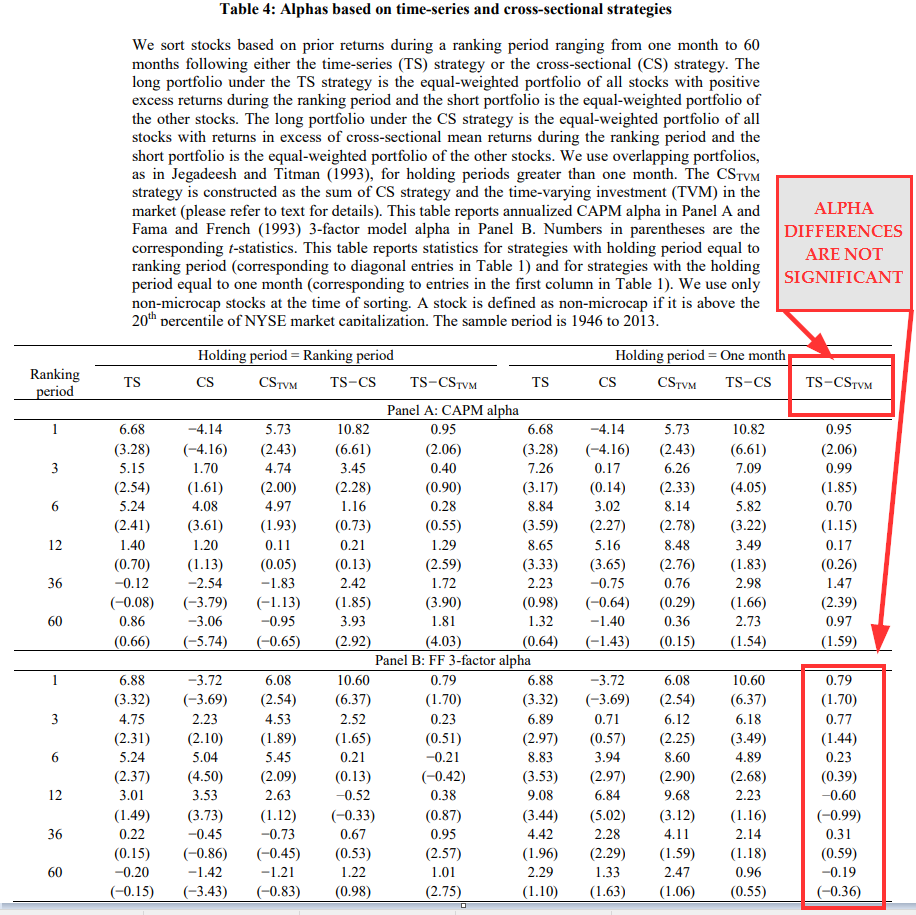
How to Turn CrossSectional into TimeSeries Momentum (and be home in time for dinner)
Panel data, also known as longitudinal data or cross-sectional time series data, refers to data that contains observations on multiple entities or individuals over a period of time. Each entity is observed repeatedly, allowing for the analysis of both cross-sectional and time series variations. Panel data can be structured in a balanced or.

multiple regression ISPSS Crosssectional time series analysis Cross Validated
Here, we are interested in time-series cross-sectional models, which have multiple series. All of the issues mentioned above get much more complicated in TSCS data becuse there are, in effect, many different time-series that we're trying to model simultaneously. Further, the parameters are often constrained to be the same across the different.
Perbedaan Data CROSS SECTIONAL, TIME SERIES, dan PANEL YouTube
As a consequence, cross-sectional evidence can only be said to be consistent with a diffusion process; it cannot definitively demonstrate that diffusion has occurred. To gain greater leverage in the diagnosis of spatial diffusion we ideally would wish to have observations arrayed over both space and time (see also Franzese and Hays 2007).