
Complementarity of Xray attenuation and darkfield radiography. Xray... Download Scientific
Overview. An X-ray is a quick, painless test that produces images of the structures inside your body — particularly your bones. X-ray beams pass through your body, and they are absorbed in different amounts depending on the density of the material they pass through. Dense materials, such as bone and metal, show up as white on X-rays.

A schematic illustration of xray medical imaging performance. Figure... Download Scientific
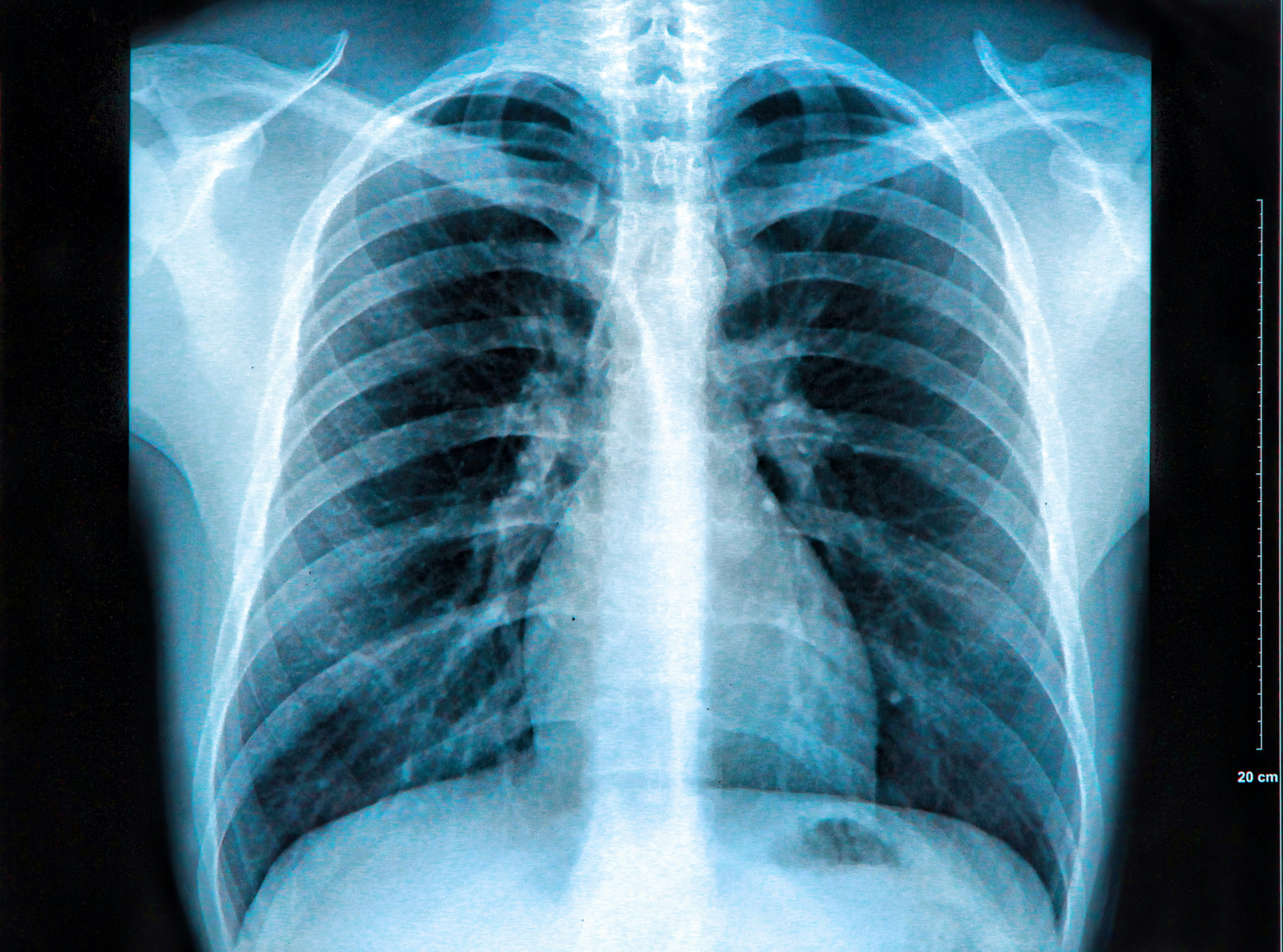
Normal chest x ray. Radiological anatomy is where your human anatomy knowledge meets clinical practice. It gathers several non-invasive methods for visualizing the inner body structures. The most frequently used imaging modalities are radiography (X-ray), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).X-ray and CT require the use of ionizing radiation while MRI uses a magnetic.
Xray Illustration Mr. Fatta
Attributions. Fig 3.3 X-ray Tube by Kieranmaher is in the Public Domain. Fig 3.4 X-ray Tube.Lead Housing with Portal for x-ray Emission, bench top image by Rschiedon is available under a CC-BY-SA 3.0 Unported License.. Fig 3.5 X-ray Image Creation and Display by Dr. Brent Burbridge MD, FRCPC, University Medical Imaging Consultants, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan is used under.
X RAY DIAGRAM WITH DETAIL Bloggjhedu
X-ray, electromagnetic radiation of extremely short wavelength and high frequency, with wavelengths ranging from about 10^-8 to 10^-12 metre. The passage of X-rays through materials, including biological tissue, can be recorded. Thus, analysis of X-ray images of the body is a valuable medical diagnostic tool.
The Science Behind XRay Imaging
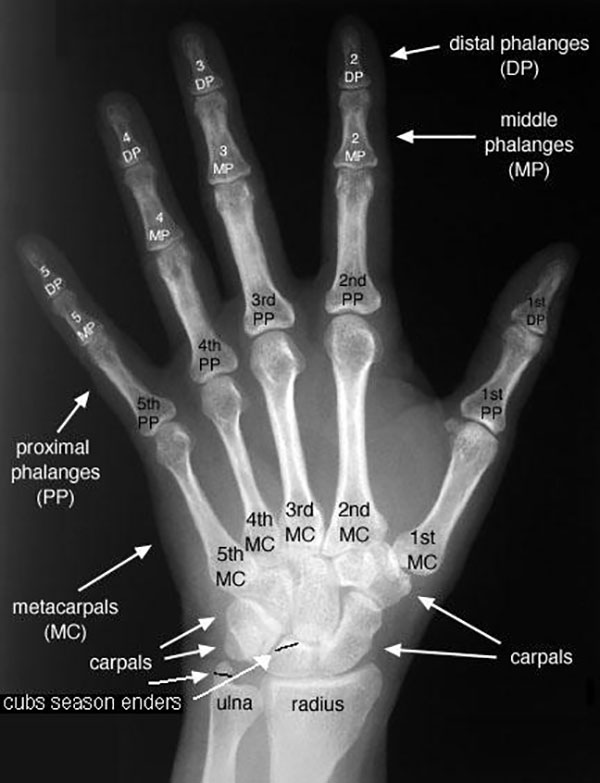
Interpreting an X-Ray. The interpretation of an x-ray film requires sound anatomical knowledge, and an understanding that different tissue types absorb x-rays to varying degrees: High density tissue (e.g. bone) - absorb x-rays to a greater degree, and appear white on the film. Low density tissue (e.g the lungs) - absorb x-rays to a lesser.

Lateral Chest X Ray Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The 'first light' observations of this gas by JAXA's X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission ( XRISM) are now ready. They demonstrate that the mission will play a big role in unveiling the evolution of the Universe and the structure of spacetime. XRISM's first test images show a cluster of galaxies and a supernova remnant - the husk left.
How To Use These Types of Xrays Wholesale Xray Film
Natural color X-ray photogram of a wine scene. Note the edges of hollow cylinders as compared to the solid candle. William Coolidge explains medical imaging and X-rays.. X-ray (or much less commonly, X-radiation) is a high-energy electromagnetic radiation.In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895.

Radiology Chest Xray Normal Radiology, Radiology student, Medical anatomy
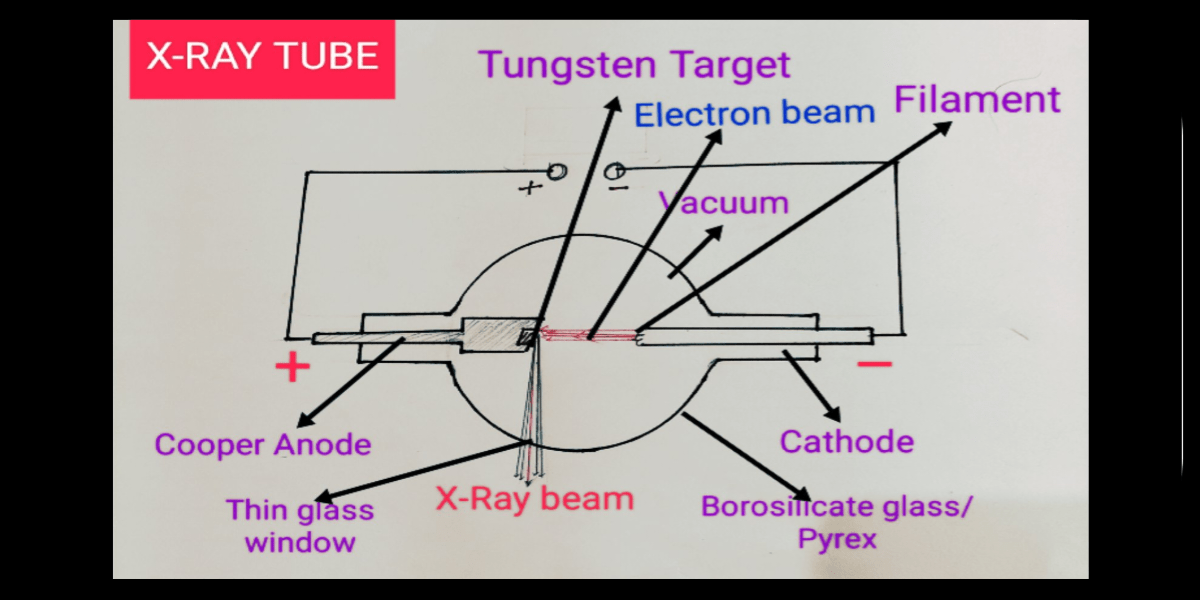
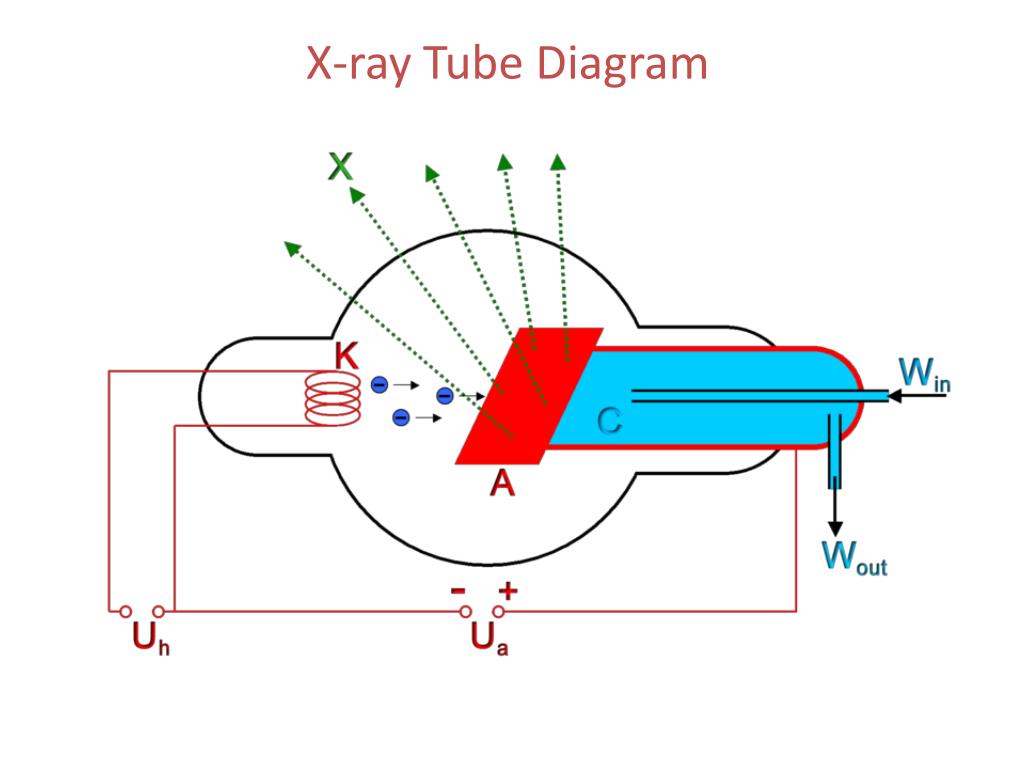
Diagram of an x-ray tube. Cathode. Filament. Made of thin (0.2 mm) tungsten wire because tungsten: has a high atomic number (A 184, Z 74) is a good thermionic emitter (good at emitting electrons) can be manufactured into a thin wire; has a very high melting temperature (3422°c)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-an-x-ray-1192147-8d86ed793e6649e6943b35c8accf0cea.png)
XRays Uses, Procedure, Results
X-ray of the chest (also known as a chest radiograph) is a commonly used imaging study, and is the most frequently performed imaging study in the United States.It is almost always the first imaging study ordered to evaluate for pathologies of the thorax, although further diagnostic imaging, laboratory tests, and additional physical examinations may be necessary to help confirm the diagnosis.
/studio-shot-of-chest-x-ray-136595862-595bdb493df78c4eb6a38dce-5c59d3ecc9e77c000132accf.jpg)
X Ray Definition and Properties (X Radiation)
Figure 2: Block Diagram of X-Ray Operation/Working of X-Ray Machine High voltage source and high voltage transformer. High voltage source is responsible for providing high voltage to the H.V transformer for a decided time. The H.V transformer produces 20 KV to 200 KV at the O/P. These voltages are used to determine the contrast of the image.

Diagram Of X Ray Tube
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first look at X-ray cosmos. Supernova remnant N132D lies in the central portion of the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy about 160,000 light-years away.
PPT Xray Tube Diagram PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2571051
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light. Unlike light, however, x-rays have higher energy and can pass through most objects, including the body. Medical x-rays are used to generate images of tissues and structures inside the body. If x-rays traveling through the body also pass through an x-ray detector on the.

Chest XRay Interpretation Checklist Outline ALL bones Check GrepMed
X-rays are a type of radiation called electromagnetic waves. X-ray imaging creates pictures of the inside of your body. The images show the parts of your body in different shades of black and white. This is because different tissues absorb different amounts of radiation. Calcium in bones absorbs x-rays the most, so bones look white.
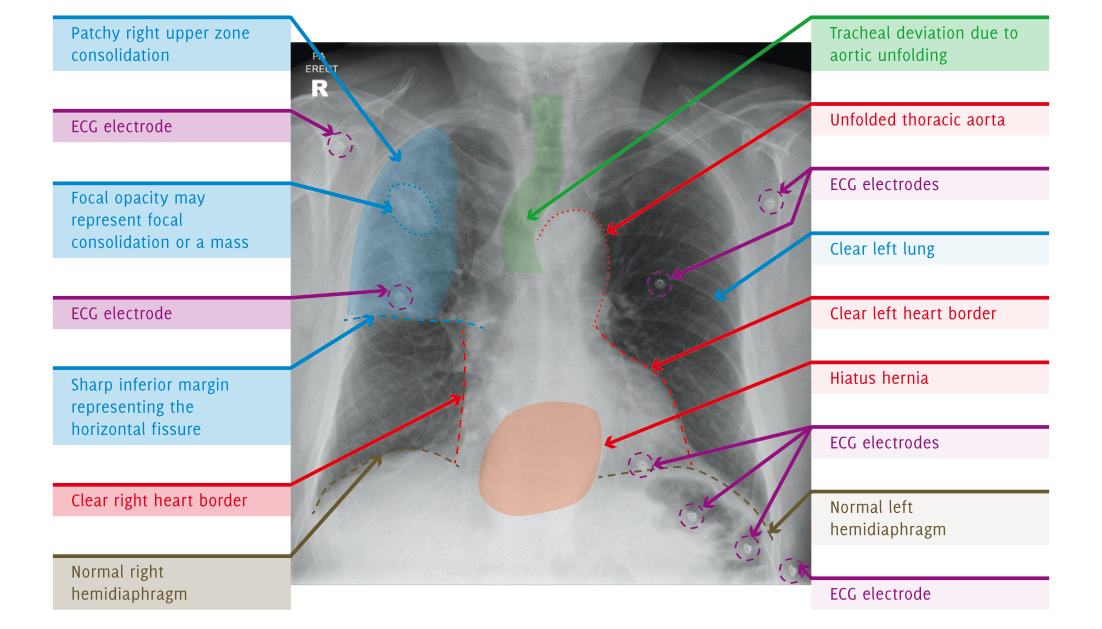
The Unofficial Guide to Radiology 100 Practice Chest Xrays
X-rays are made by using external radiation to produce images of the body, its organs, and other internal structures for diagnostic purposes. X-rays pass through body structures onto specially-treated plates (similar to camera film) or digital media and a "negative" type picture is made (the more solid a structure is, the whiter it appears on the film).

Pin on Xray A&P
X-ray: [noun] any of the electromagnetic radiations that have an extremely short wavelength of less than 100 angstroms and have the properties of penetrating various thicknesses of all solids, of producing secondary radiations by impinging on material bodies, and of acting on photographic films and plates as light does.

Uses of Radioisotopes Chemistry for Majors
X-rays are produced by interaction of accelerated electrons with tungsten nuclei within the tube anode. Two types of radiation are generated: characteristic radiation and bremsstrahlung (braking) radiation. Changing the X-ray machine current or voltage settings alters the properties of the X-ray beam. X-rays are produced within the X-ray.